What Is MIG Welding?

MIG welding is a specific type of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) that’s effective at welding a variety of different metals together. MIG stands for ‘metal inert gas’, a reference to the inert or non-reactive gases needed to shield the weld pool during the MIG welding process.
MIG welding results in highly precise, high-quality welds, and it’s a process that’s been adopted across many industries. A MIG welder is particularly well suited to welding thin gauge metals such as aluminium or magnesium, over which the welder needs a high degree of control over the process.
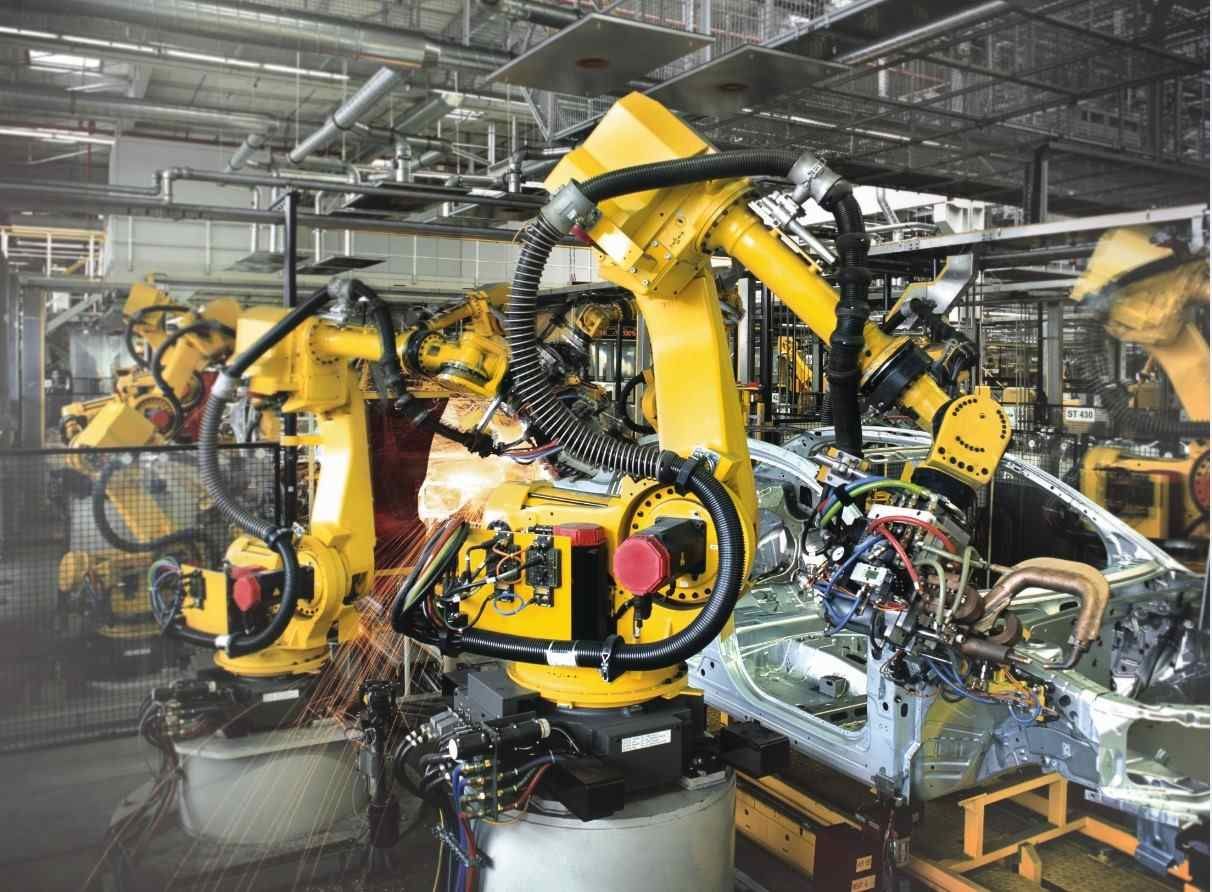
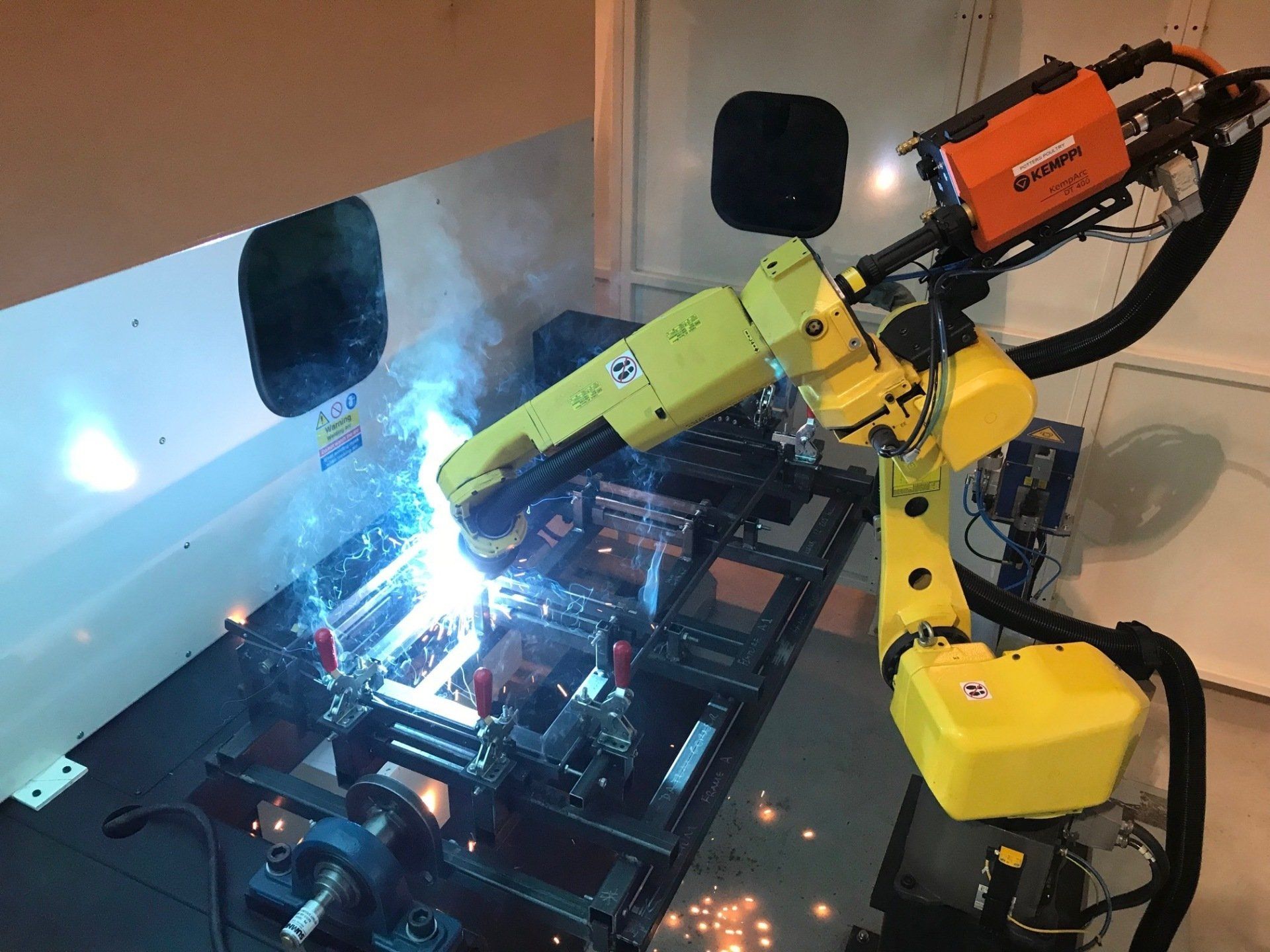
The MIG welding process is easily automated through the use of robotic systems, ensuring that an already robust welding process can produce consistent and accurate results, while reducing waste and improving health and safety in the workplace.
What Is MIG Welding?
MIG welding is an acronym for metal inert gas welding, a specific type of welding requiring an inert gas to work. The MIG welding process is a sub-type of gas metal arc welding (GMAW), which also includes MAG welding, or ‘metal active gas’ welding, under its broader umbrella.
MIG welding is a type of arc welding. The MIG welding process uses an electric arc to produce the high temperatures required to create a weld pool that can fuse metal materials together. This weld pool must be protected through the use of an inert gas, which effectively forms a shield that prevents oxidation and stops any outside contamination interfering with the temperature or causing unwanted reactions.
The choice of inert gas is integral to the MIG welding process. This is where it varies considerably in relation to other forms of arc welding, such as MAG welding. MIG welding uses inert gases, such as neon or argon, because inert gases are non-reactive. An inert gas molecule has an outer layer of electrons around it. This is called a valence. That valence protects the gas from reacting with other elements in the atmosphere. Using an inert gas as a shield means that the welding process is protected from reactions that would otherwise affect the quality of the weld or extinguish the arc.
There are several different types of inert gas that can be used in the welding process, including noble gases. All noble gases are inert gases and are particularly unreactive. However, noble gases are rare and expensive, so costs can be lowered by using a gas compound that might contain a mixture of noble and active gases instead.
The most effective inert gases for MIG welding include:
● Helium
● Neon
● Argon
● Krypton
● Xenon
● Radon
MIG welding results in higher quality and more precise welds compared to MAG welding, which uses an active gas compound that is more reactive and therefore offers less protection. This means that MIG welding is often utilised in order to weld together thinner, more reactive metals like aluminium, which require strict atmospheric controls and consistent temperatures in order to be welded.
MIG welding is one of the most effective forms of welding, but it takes skill and experience to handle a MIG welder manually. MIG welding is a costly process too, although it results in less waste and a higher quality product when used effectively. In this respect, automating the MIG welding process helps to remove many of these disadvantages, with automated, robotic MIG welding being one of the best forms of welding available.
How Does MIG Welding Work?
So what’s the MIG welding process? MIG welding is a process first invented in 1948. Since then, the basics have stayed essentially the same, despite the equipment involved having been vastly improved.
The process of MIG welding is very standardised, and the basic tools, equipment and techniques vary little from one industry or application to another. This is another reason why MIG welding processes can easily be automated, as the techniques can be replicated consistently through robotic integration.
Here are the essential components required in order to MIG weld:
● Inert shielding gas or compound gas
● Weld gun
● Electric arc
● Consumable wire filler
● Power source
● Safety equipment
Regardless of whether you are MIG welding by hand or have a fully integrated and automated MIG welding system set up on a production line, you’ll need all of the above components in order to weld.
The electric arc is produced using electricity and controlled by a welding gun. The electric arc ignites a consumable wire filler; this melts both the filler and the material being welded, creating a weld pool. The wire needs to be continually fed into the weld gun, as it’s burned through during the welding process.
While this occurs, the weld pool is being shielded from oxidation and contamination through the use of the shielding gas. The shielding gas is fed into the weld gun through a nozzle, and into the same supply tube in which the consumable wire is held.
Once the weld pool has formed, it will cool down and solidify when the temperature is lowered. Remove the heat and the weld pool solidifies; it’s this process that allows two different pieces of metal material to be fused together.
A modern welding machine has all of these components integrated into its system. For manual welding, the weld gun provides a way to control the heat and application of the consumable filler and gas, while making the weld. This process can be completely automated through the use of robotic MIG welding equipment.
Robotic MIG Welding for Beginners
Manual welding is a process that requires a high degree of skill, precision and accuracy. It takes a long time to train a manual welder to produce consistent, high-quality results, particularly given the potential hazards involved.
MIG welding requires intense levels of concentration on the part of the manual worker, and it’s often carried out in stressful, industrial environments. Extreme heat and industrial equipment make any welding process a hazardous task, and mistakes can lead to serious injury or worse.
But robotic MIG welding technology has advanced to such a point that automated systems can carry out welding tasks so consistently that the need for manual welding can be avoided. Automated MIG welding can be carried out faster than manual welding, while the results are just as consistent, if not better, than the results produced by an experienced human operator. Robotic MIG welding makes the workplace safer and allows human staff to concentrate on other tasks, while improving efficiency and lowering costs.
The main advantages of a robotic MIG welder include:
● Improved welding standards
● Greater speed and efficiency
● High degrees of accuracy and precision
● Less waste
● Ability to operate 24 hours a day
● Higher standards of workplace safety
● Improved cost-effectiveness
A robotic MIG welding system requires all of the components of manual MIG welding, including a welding gun, electric arc, a shielding gas, power source and consumable wire filler. Rather than being operated manually however, the weld gun is attached to a robotic arm. This can be programmed to carry out the required welding task, and can be integrated into wider systems such as a conveyor belt or production line.
What Is MIG Welding Used For?
MIG welding has an impressive number of advantages compared to other types of welding, which ensures that there is also an impressive range of applications for the process.
These advantages include:
● Weld pools are protected from oxidation
● Weld pools are protected from reactions
● Consistent temperatures can be maintained
● A high-quality weld is produced
● MIG welders can be automated with robotic systems
These benefits mean that MIG welding has a wide variety of applications. The welding process can be used to fuse a multitude of different metal materials together, and the process has been adopted by many industries worldwide. A few of the industries and professions that use MIG welding include:
● Aerospace
● Automotive
● Construction
● Design
● Manufacturing
● Mechanics
● Shipyards
Within these industries, a MIG welder can be used for a variety of tasks and purposes. For example, MIG welders may be needed to assemble machinery components on a conveyor belt, or they may be required for repair work on a Boeing 747.
MIG welding can be utilised at various stages in the manufacturing or construction process. For example, a MIG welder may be used in the manufacturing stage of a car, where a robotic MIG welding machine can be integrated into a car assembly line. They may also be needed for maintenance purposes, ensuring that equipment or products can be repaired or upgraded where necessary.
What Metals Can You MIG Weld?
A MIG welding machine is well suited to welding a wide variety of different metals together, and it’s one of the most versatile welding methods available. For this reason, MIG welding machines have been adopted by a wide variety of different industries and sectors across the world, ranging from car manufacturing to product design.
But to make the most of the unique qualities of a MIG welding machine, there are certain types of metal that are best welded with a MIG welder and others that are best avoided.
Because a MIG welding machine uses inert gas to protect the weld pool, it creates incredibly consistent conditions for welding. This means that MIG welding is perfect for producing consistent temperatures, and for protecting the weld pool from oxidation or other unwanted reactions that would spoil the quality of the weld. MIG welding is the best way to weld aluminium, for example, which is easily damaged by oxidation if conditions aren’t exactly right.
But MIG welding isn’t well suited to thick, higher gauge metals such as steel. It’s best suited for thinner, lower gauge metals that don’t require such high temperatures to be welded. The best metals for welding with a MIG welder include:
● Aluminium
● Magnesium
● Copper
● Nickel
MIG welders are highly adaptable, though. For thicker materials such as steel, a MIG welder can be effective if the type of gas used is a compound. Rather than simply using an inert gas, a noble gas can be mixed with an active gas such as oxygen. While the MIG welder would lose some of its protection due to the change in shielding gas, compound gases would result in higher temperatures that weld thicker materials. This is fine if the metal in question, like steel, doesn’t need as much protection from oxidation or contamination during the welding process.
What Is the Difference Between a MIG and TIG Welder?
There are several other common types of industrial welding, other than MIG welding. One such welding process is TIG welding, which also uses an inert gas as a shield.
TIG welding stands for ‘tungsten inert gas’ welding and, like MIG welding, it’s also a form of GMAW (gas metal arc welding). TIG welding requires a non-reactive, inert gas in order to protect the weld pool from contamination, and similar noble gases such as argon or helium can be used.
The primary difference between MIG and TIG welding is the fact that TIG welding processes require tungsten. Whereas MIG welding uses a consumable filler wire – usually a metal such as aluminium – TIG welding uses tungsten as a non-consumable filler. This means that when the electric arc is burning, the tungsten isn’t consumed and therefore doesn’t need continually replacing (at least in the short term).
TIG welding creates a stronger, more durable weld than MIG welding, and it can be used to weld together thicker, stronger materials (including steel). However, TIG welding has more variables, and it’s a slow welding process in comparison to MIG welding, which is better suited to high-volume welds.
Contact Cyber-Weld Today for More Information on Automated MIG Welding Solutions
If you’d like to know more about the automated MIG Welding process, our expert team of robotic engineers are ready to help.
Cyber-weld provides a comprehensive range of MIG welding processes, alongside an extensive array of bespoke robot welding solutions designed to fulfil your automated welding needs.
Contact Cyber-Weld today to find out how we can help you.