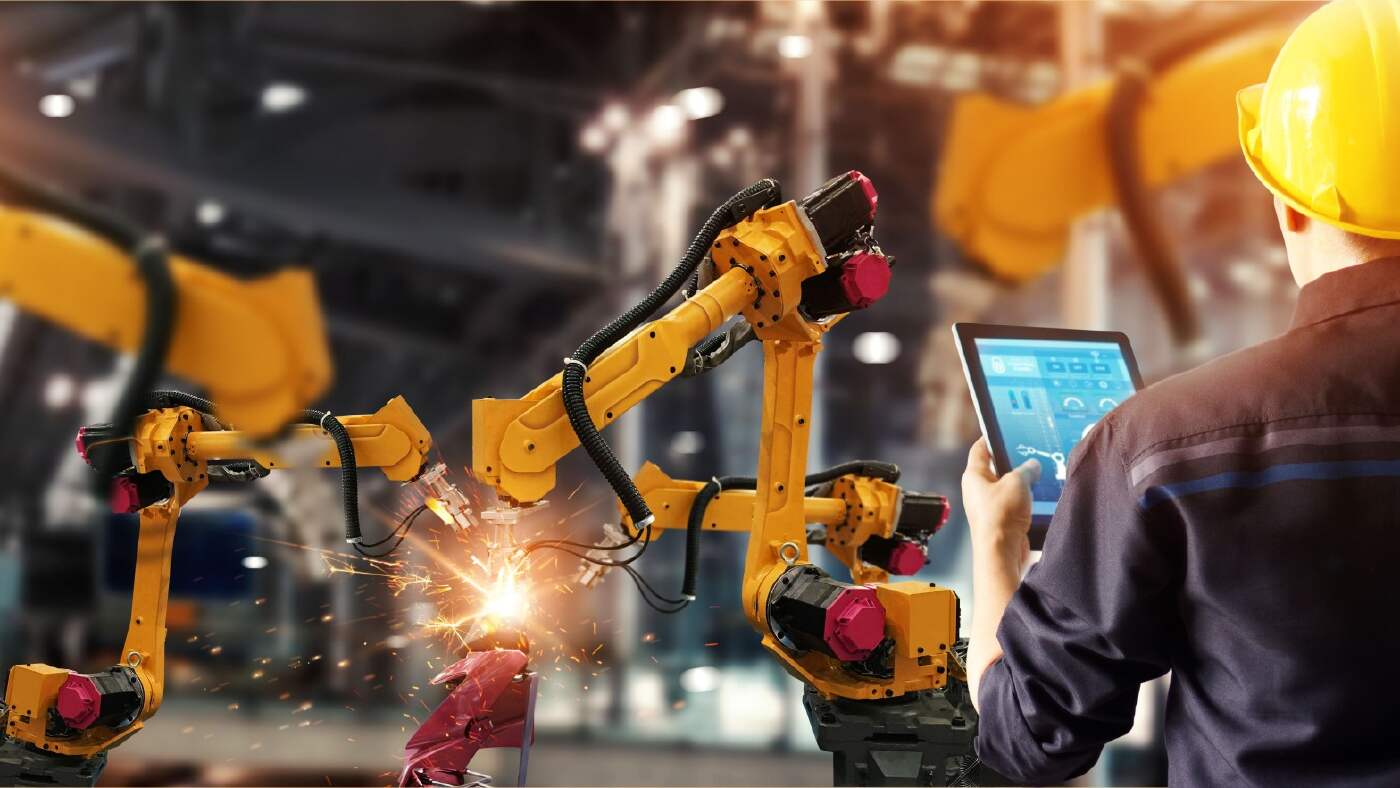
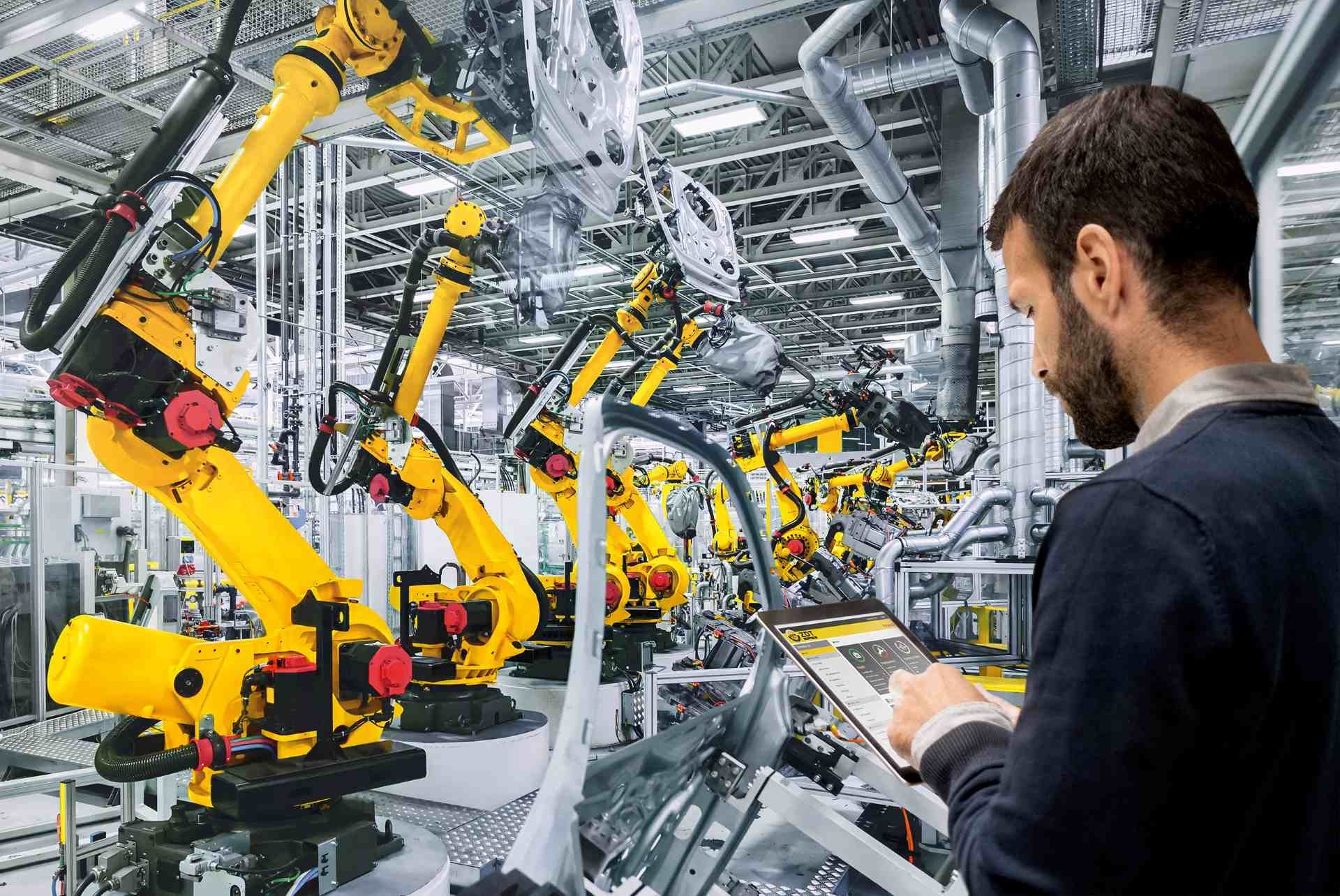
Robotic Welding Processes
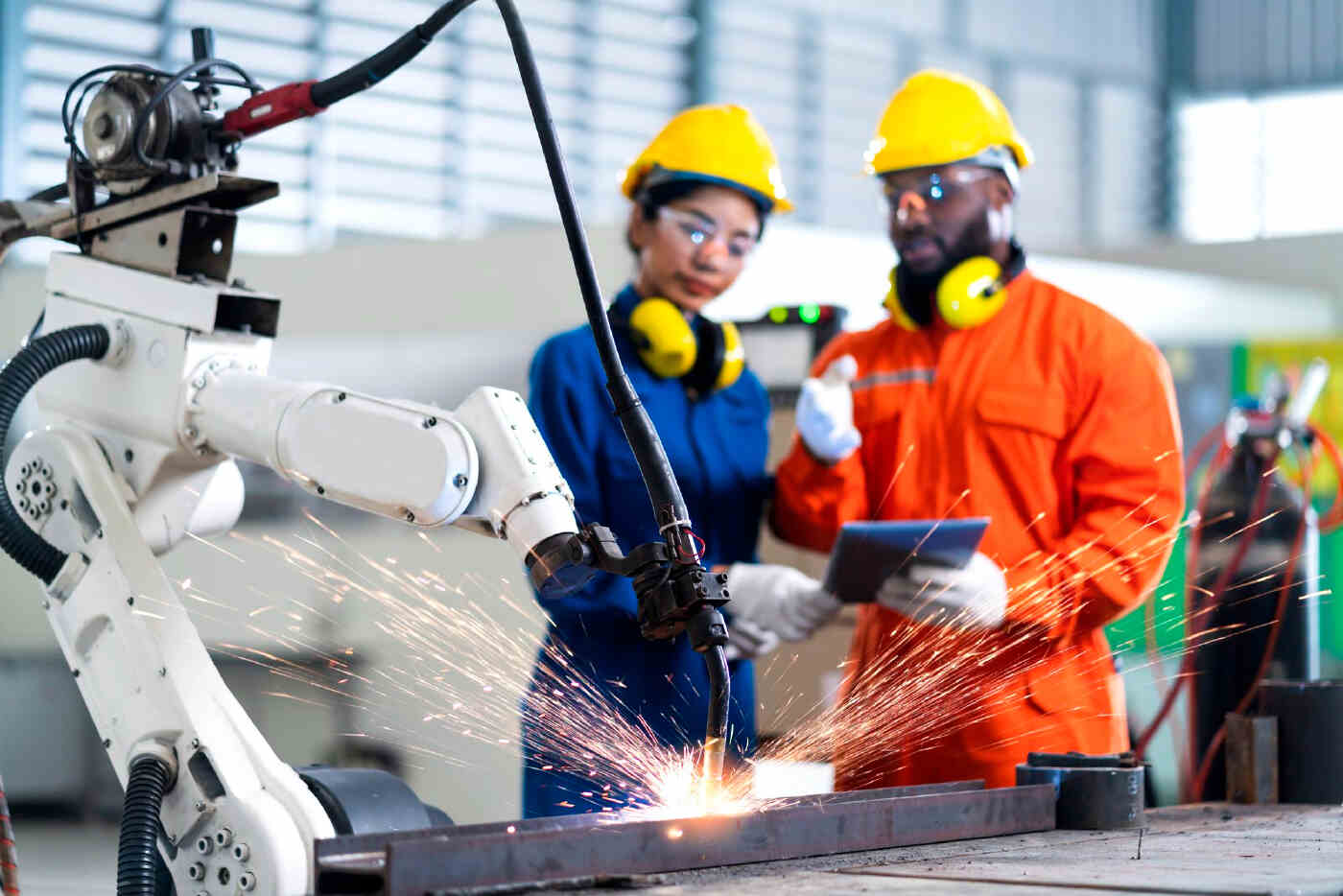

Robotic welding processes are an effective way to automate the manual welding process, thereby improving efficiency, productivity, accuracy, and health and safety in the workplace.
Automated welding processes can be designed to integrate existing welding processes, such as MIG and MAG welding, TIG welding, plasma cutting, and more.
If you’re planning to automate your welding systems, the team at Cyber-Weld is here to explain everything you need to know about robot welding processes.
Can Welding Be Automated?
Traditional manual welding is a process that requires a high level of skill, experience and accuracy on the part of the welder. It’s a job that’s often hazardous, but also one that’s repetitive and requires high levels of concentration.
This means that the manual welding process is a process that’s well suited to automation. Welding processes can be integrated into robotic welding systems, leading to a number of excellent advantages over manual welding.
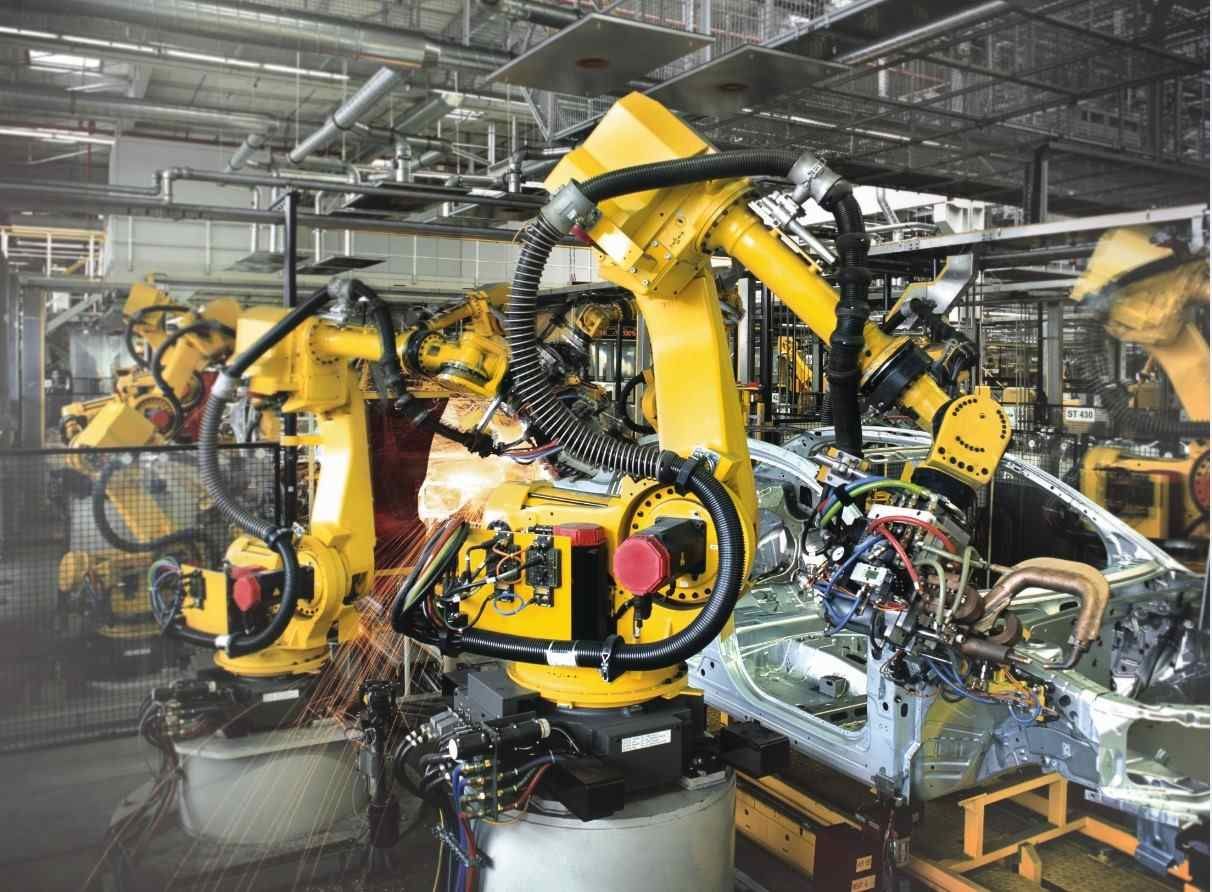
In fact, automated welding processes are already well established in many industries across the world. Robotic welding is a mainstay of car assembly lines, as well as aviation, construction, manufacturing and many other industries.
Robot welding systems offer an impressive number of advantages over traditional, manual welding, ensuring that automated welding processes continue to be adopted. The most important advantages of automated welding processes include:
● Improved efficiency
● Improved speed
● Greater accuracy and precision
● Cost-efficiency
● Improved workplace safety
● Ability to operate 24/7
What Is Automation in Welding?
Automation is the process of making a system operate automatically, with little or no human interference. Automation in welding is therefore the process of making a welding system run automatically, without the need for human operation and with the need for little human supervision.
The welding process can be effectively automated with the use of robot welding systems. This occurs best through the use of advanced robotic arms. In practical terms, this means that a welding system is attached to a robot arm, which is then programmed to perform the welding tasks allocated to it.
Automation in welding is an excellent way to improve efficiency, improve accuracy and precision, decrease costs, reduce waste and improve workplace health and safety. An automated welding system can effectively complete the same welding tasks as a human, but with much-improved quality standards.
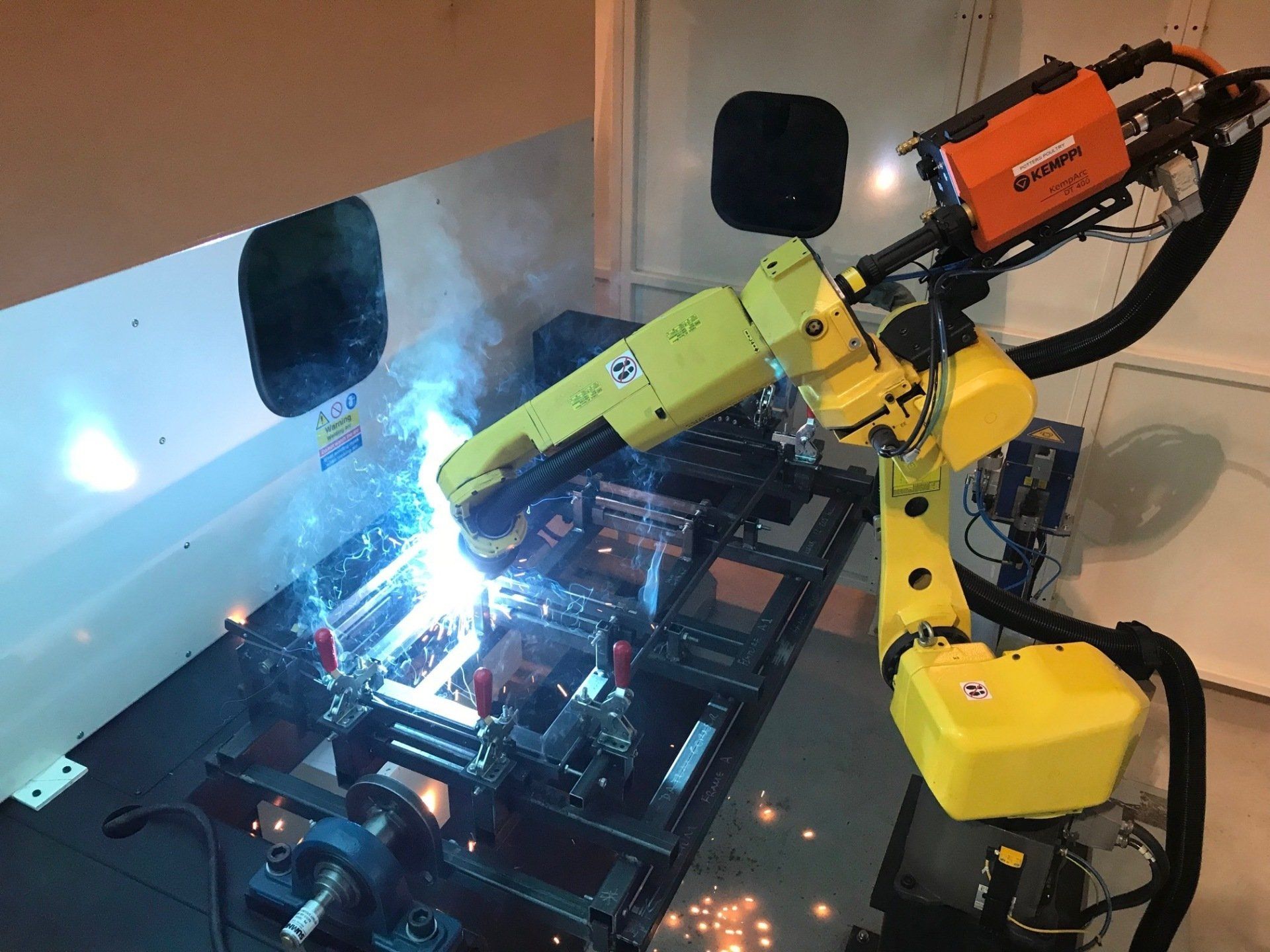
How Robotic Welding Works
Robotic welding requires several key elements designed to work together, which allow it to be an effective, automated system.
The primary requirement of a robot welding system is a robotic arm which has the capacity to be equipped with welding tools and equipment. The exact tools depend on the type of robotic welding being carried out, but will include a heat torch and some form of consumable wire filler.
The robotic arm can produce the heat required to create a weld pool, and the process can be shielded using different types of gas. On top of this, the robotic welding system will require programming in order to carry out its tasks and may be integrated into wider systems (such as conveyor belts on manufacturing lines, for example).
Most Popular Robotic Welding Processes
There are a number of different welding processes that are commonly used to fuse metals and materials together. This includes the effective GMAW (gas metal arc welding) process, for example, of which there are several popular sub-varieties.
Because of the high degree of accuracy that can be achieved, a robot welding process is well suited to welding difficult metals such as aluminium, which require stringent conditions and precision to be safely welded.
Almost all manual welding processes can be fully automated with excellent results, but the most popular robot welding processes include:
Let’s explore these in more detail:
Robotic MIG Welding
Robotic MIG welding is a specific type of GMAW (gas metal arc welding) designed to use an electric arc and a consumable filler to create a weld pool that fuses two metals together.
MIG stands for ‘metal inert gas’, and MIG welding requires the use of an inert or unreactive gas (such as helium or argon) in order to create a shield. This shield protects the weld pool from outside contamination, allowing for high temperatures to be sustained and a seamless weld to be produced.
MIG welding is exceptionally accurate and precise, and is well suited to welding thin gauge metals or metals such as aluminium, which require very particular environmental conditions to be welded.
Robotic MAG Welding
Robotic MAG welding is also a specific type of GMAW (gas metal arc welding). MAG welding uses an active gas rather than an inert gas in order to shield the weld pool. MAG welding uses gases such as oxygen or carbon dioxide, which ensures that it’s a more cost-effective process than MIG welding.
Robotic MAG welding is one of the most common automated welding processes. Automation ensures that MAG welding can be carried out more accurately, allowing for precise, high-quality results that can be produced consistently.
Robotic TIG Welding
Robotic TIG welding is another popular automated welding process that allows for a highly accurate and precise weld to be produced. This is a form of arc welding that also uses gas to create a shield, and ‘TIG’ stands for ‘tungsten inert gas’.
TIG welding differs from MIG welding, because it uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode in order to create a weld pool. TIG welding is also exceptionally accurate, particularly when it’s integrated into a robotic welding system
Robotic Plasma Cutting
Other types of robotic welding processes include:
● Resistance welding
● Laser welding
● Spot welding
● Thin gauge arc welding
● Plasma cutting
Robotic welding processes can also be integrated into wider robotic systems (for example, alongside, maintenance, pick and pack, or palletising robots on a construction line) allowing for the complete automation of manufacturing and construction work.
Contact Cyber-weld Today for More Information on Robotic Welding Solutions
If you’d like to know more about automated welding processes then our expert team of robotic engineers are ready to help.
Cyber-weld provides a comprehensive range of robotic welding services, alongside an extensive array of bespoke robot welding solutions designed to fulfil your automated welding needs.
Contact Cyber-Weld today to find out how we can help you.