Robotics in the Manufacturing Industry

Offering speed, versatility and accuracy, robots are an integral component of production and manufacturing industries across the world. From exceptional precision in the initial design stage, right through to the assembly of parts on the production line, manufacturing robots offer a level of efficiency and ease unrivalled by their human counterparts.
In this article, we explore the history of robots and manufacturing, before explaining the different types of manufacturing robots, their benefits and uses, and their potential to replace humans in the workplace. Here’s everything you need to know about robotics in the manufacturing industry.
Robotics and Manufacturing
Ever-improving technology ensures that robots have become an important part of industrial production and manufacturing processes. Robots have allowed previously mundane or difficult tasks to be partially or fully automated, thereby improving the consistency of manufactured products while allowing the production processes to become more streamlined.
Importantly, robot-manufacturing systems have led to improvements in workplace safety, allowing potentially dangerous jobs to be fully automated. These benefits can be realised throughout the manufacturing process, with robots commonly employed in the design stage of a product, right through to the packaging and dispatching of items to customers.
Manufacturing robots are incredibly diverse and can be found performing an impressive range of tasks, including:
- Assembly
- Design
- Inspection
- Material handling
- Packaging
- Painting
- Palletising
- Testing
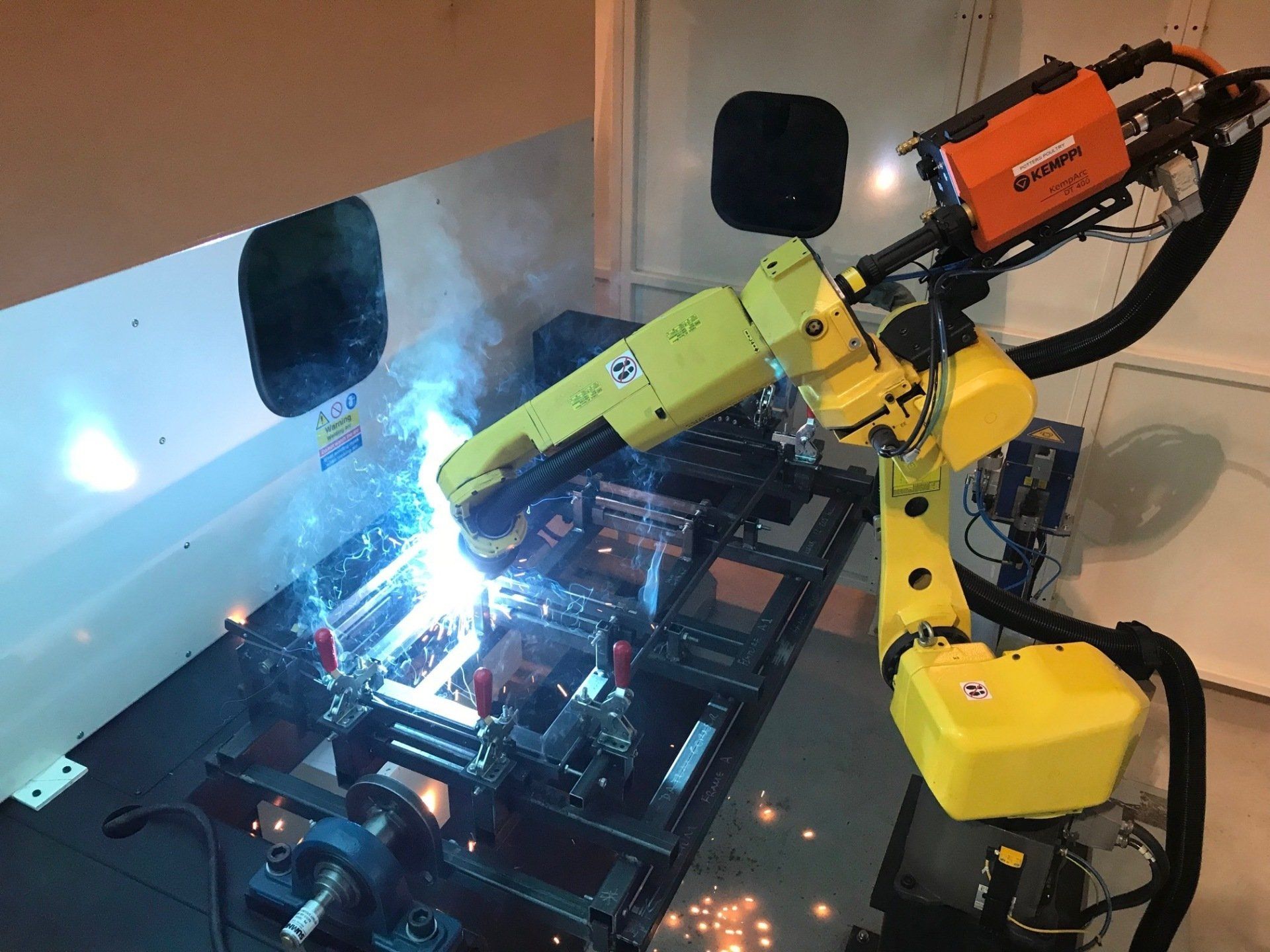
- Welding
They are also found across an impressive range of industries. For example, manufacturing robots are commonly utilised by car manufacturing companies, in the aerospace industry, by pharmaceutical companies, and on warehouse floors by retail and distribution companies. If a task is monotonous, if it requires precision or is dangerous, then it has the potential to be automated through integrated robots and manufacturing systems.
Of course, this increasing reliance on robots in the manufacturing industry has led some to question the future of robotics. Automation can replace human jobs, but there are many ways that human workers stand to benefit from robotic manufacturing, too.
History of Robotics in Manufacturing
American inventor George Devol designed the first automated manufacturing robot in the 1950s, creating a machine named ‘Unimate’ (derived from the term ‘universal automation’) that became popular on car assembly lines. Unimate paved the way for the manufacturing robots we have today, but the history of robotics goes back much further than this.
The Ancient Greeks theorised about the possibility of creating ‘automata’, or entities or machines that could take over manual tasks and free up time for humans to focus on other pursuits. The Arabs developed automated clocks and gears from the 5th century AD onwards, while Leonardo Da Vinci drew up plans for an automated knight complete with armour and weapons in Renaissance-era Italy.
It was during the Industrial Revolution that the concept of automated manufacturing – which in turn led to the modern idea of robotic manufacturing – really took off. As manufacturing demands increased, production processes became more mechanical. By the 1900s, the concept of robotics was forming, as designers and inventors began imagining and building basic humanoid-style machines.
In 1939, a robot in human form made an appearance at the World’s Fair, and in the 1940s, Isaac Asimov created his now-famous Laws of Robotics. Industrial robots were developed in the 1950s with computational abilities, and alongside this advancement began the development of more humanoid robots.
In the 21st century, the reality of a fully automated, artificially intelligent humanoid robot has been advanced hugely. Manufacturing robots have improved greatly, and today they are capable of being programmed and designed to perform tasks across a wide range of industries, with a degree of precision that humans simply cannot achieve.
While many of the first manufacturing robots were designed and built by American companies, the focus has shifted to Asia (in particular, Japan), where industry-leading robotics manufacturers such as FANUC lead the way.
When Was the First Robot Used in Manufacturing?
Today, millions of robots perform tasks daily in manufacturing roles worldwide, but the automated revolution has been through a surprisingly rapid process of development.
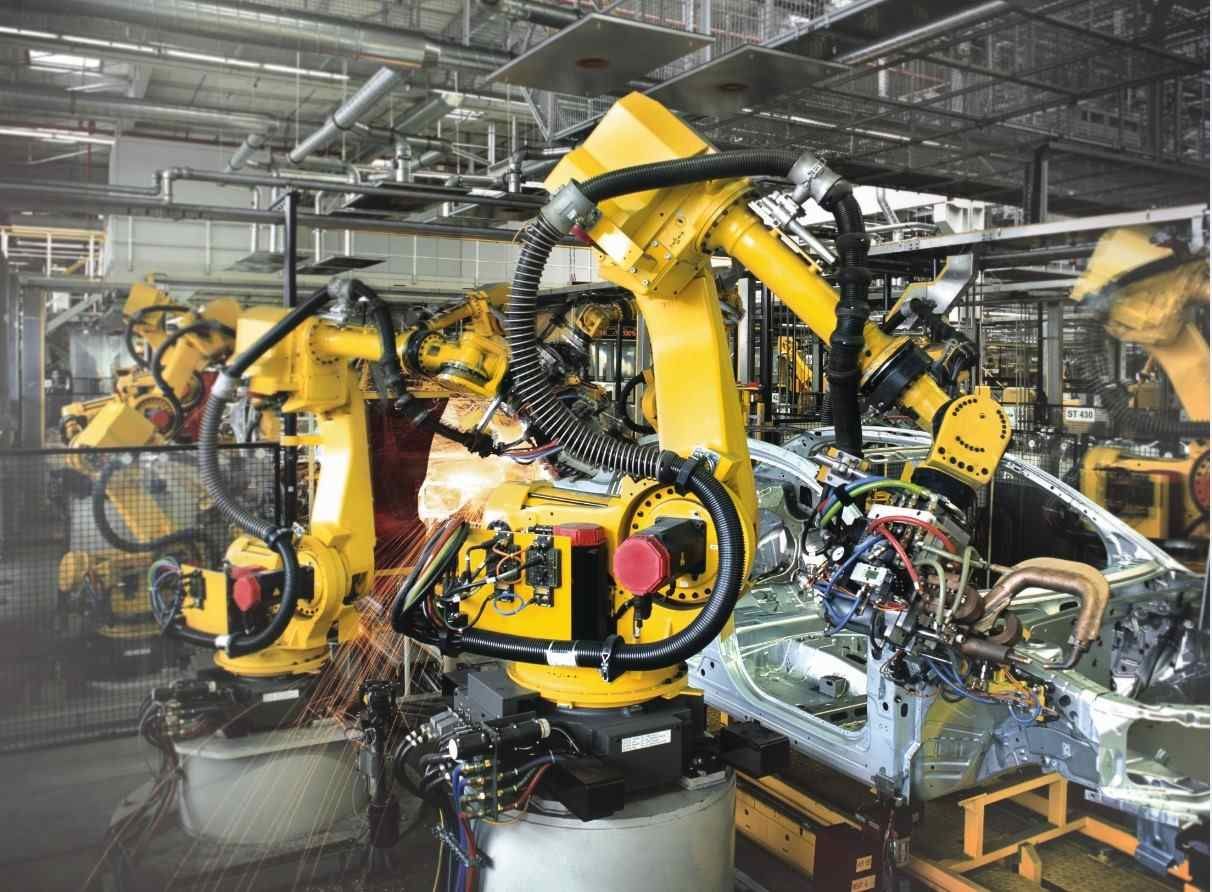
The first functional manufacturing robot is commonly said to be the industrial robot named ‘Unimate’, which was developed for car manufacturers in the US in the 1950s. Unimate moved on several axes, had basic computational abilities, and the capacity to weld parts onto cars during the assembly process.
Unimate was designed by the pioneering robotics company established by George Devol. He was granted a patent in 1961 after several years of development, and the first manufacturing robots sold soon after to General Motors. Unimate was not only a manufacturing success but a pop culture phenomenon, making appearances on prime time television shows and taking America by storm.
Unimate was developed not only as a way to speed up car manufacturing but in response to safety concerns. Unimate’s primary role was moving ‘die casts’, a job that was hazardous to human health due to the toxic nature of the components involved. Replacing this job with a robot significantly improved safety conditions in the car factories, and really began the process of automation that continues to this day.
Why Use Robots in Manufacturing?
Robots can be designed to perform a number of different tasks, and they have the potential to perform many of these tasks to a higher calibre than human workers can. Repetitive or dangerous tasks can easily be performed by a robot, allowing companies to produce higher quality products more consistently.
This versatility is one of the primary reasons that robots have become so popular in the manufacturing industry. Examples of the tasks they can be programmed to perform include:
- Welding materials
- Assembling parts and products
- Cutting and slicing
- Painting products
- Labelling products
- Picking products
- Packing products
- Testing products
- Handling materials
- Handling dangerous goods or waste
- Palletising products
Manufacturing robots can be used across a wide range of industries, and they are popular in the following sectors:
- Agriculture
- Aerospace
- Automobile
- Design
- Food production
- Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Tech and computing
There are many benefits to be realised from robots and manufacturing. The main goal of any robotic manufacturing system is often automation, but there are other advantages too, in terms of consistency, precision and health and safety.
Here are the most important advantages when combining robots and manufacturing:
- Improved efficiency: Robotic manufacturing systems improve the efficiency of production processes, reducing waste, speeding up production times and saving on manufacturing costs.
- Improved production speeds: Manufacturing robots can operate at far faster speeds than humans can in the same role. This means that more products can be produced or tasks completed at a faster rate.
- Excellent levels of accuracy and precision: Robots can be programmed to work to an incredible level of accuracy and precision that even the highest skilled manual workers fail to achieve consistently, and over long periods of time.
- Cost-effective: Robots can be run 24/7, leading to huge cost savings on assembly lines. They also lead to fewer wasted products and materials, thereby saving money.
- Improved workplace safety: Robots can replace dangerous roles in manufacturing processes, reducing the risk of injury or death to human workers. Robots also remove the need for monotonous human tasks, reducing repetitive strain injuries while leading to a happier workforce in the long term.
Types of Manufacturing Robots
Manufacturing robots are incredibly diverse, and they can range in style and design from a simple picking machine designed to remove products from a conveyor belt, right through to complex welding robots involved in car manufacturing.
Manufacturing robots will fall into one of six categories, each of which has been designed for a unique if versatile function. These are:
- Articulated robots: designed to function as a human arm, they operate on several axes and are incredibly versatile.
- Cartesian robots: also called gantry robots, they operate on x, y and z axes and are often designed for picking and packing.
- SCARA robots: ‘Selective compliance assembly robotic arm’. Designed to complete a selective and complex assembly task.
- Spherical robots: can operate up and down and all around to perform complex tasks.
- Delta robots: operate in pick-and-pack roles within a dome-shaped sphere of interaction.
- Cylindrical robots: simple robots that operate on a horizontal or linear basis.
Specific examples of manufacturing robots designed for particular tasks include:
- Mig/mag welding robots
- Tig/tag welding robots
- Material handling robots
- Assembly robots
- Pick-and-pack robots
Manufacturing robots can be designed to suit a wide variety of processes, and complex robotic systems can be tailor-made to fit your company’s manufacturing environment needs.
Future of Robotics in Manufacturing
Robots and manufacturing have advanced significantly in recent decades. Huge leaps have been made within the last 70 years, ever since the first manufacturing robots were installed on production lines in the 1950s.
The development of robotic technology, hardware, software and systems is advancing at an almost exponential rate. In this respect, the future of robotics in manufacturing is an exciting one.
Manufacturing robots are expected to become more intuitive, relying not only on their programming but on their ability to process the environment around them. This is fuelled by a growth in the artificial intelligence sector, which will provide robots with the ability to think for themselves.
Robotic developers, such as FANUC, are already designing robots that have the capacity to learn from the environment around them, and from their own actions. This means that manufacturing robots will be more self-reliant, more adaptable and will require even less human involvement in the future.
As robot-manufacturing systems become more advanced, they will become more accurate and precise. The biggest advantage to this is that they can then be used in the assembly of more complex products, such as electronics (including mobile phones, which are generally still built by hand).
As a whole, the use of robotics in manufacturing is also going to increase. More processes will become automated, existing robotic systems will be streamlined, and the quality and consistency of technology will only improve.
Can Robots Replace Human Workers in Manufacturing?
The question of human workers losing jobs to automation is one that’s been asked since the Industrial Revolution.
While robots are commonly designed to directly replace manual roles that have in the past been performed by workers on production lines, this doesn’t mean there’s necessarily going to be a loss of jobs. In fact, in the developed world, automation can help to retain and create jobs.
One of the biggest arguments in this respect is the simple economic fact that manufacturing companies already outsource labour. In most cases, it’s more cost-effective to employ someone in a low-cost country than it is to employ someone to do the same job in the UK.
Robotic manufacturing helps to keep costs low, and the upfront cost of a bespoke automation system can be recouped quickly. This enables companies to automate their manufacturing process at home, rather than being forced into outsourcing. This enables jobs to be retained, and employees can be retrained or upskilled and kept on at the company.
Automation also helps companies to diversify and innovate. In the same respect, employees now have more time to spend on other projects, rather than spending all day performing monotonous assembly and manufacturing tasks.
Ultimately, automating manual or dangerous work enables a country to switch to a higher-skilled and higher-paying economy while remaining competitive.
Contact Cyber-Weld Today for More Information on Robots and Manufacturing
If you’re looking to automate your production and manufacturing processes, the expert team at Cyber-Weld is here to help. Our experienced engineers are specialists in designing and building bespoke manufacturing robots across an impressive range of industries.
We can provide a full-service robotic manufacturing system, tailor-made to meet your industrial needs. Our friendly staff will be there at every stage of the process, from the initial concept and planning stage, right through to after-sales and robot servicing and support. To find out more about our services, contact our qualified team at Cyber-Weld today.