Robotics in Aerospace Engineering

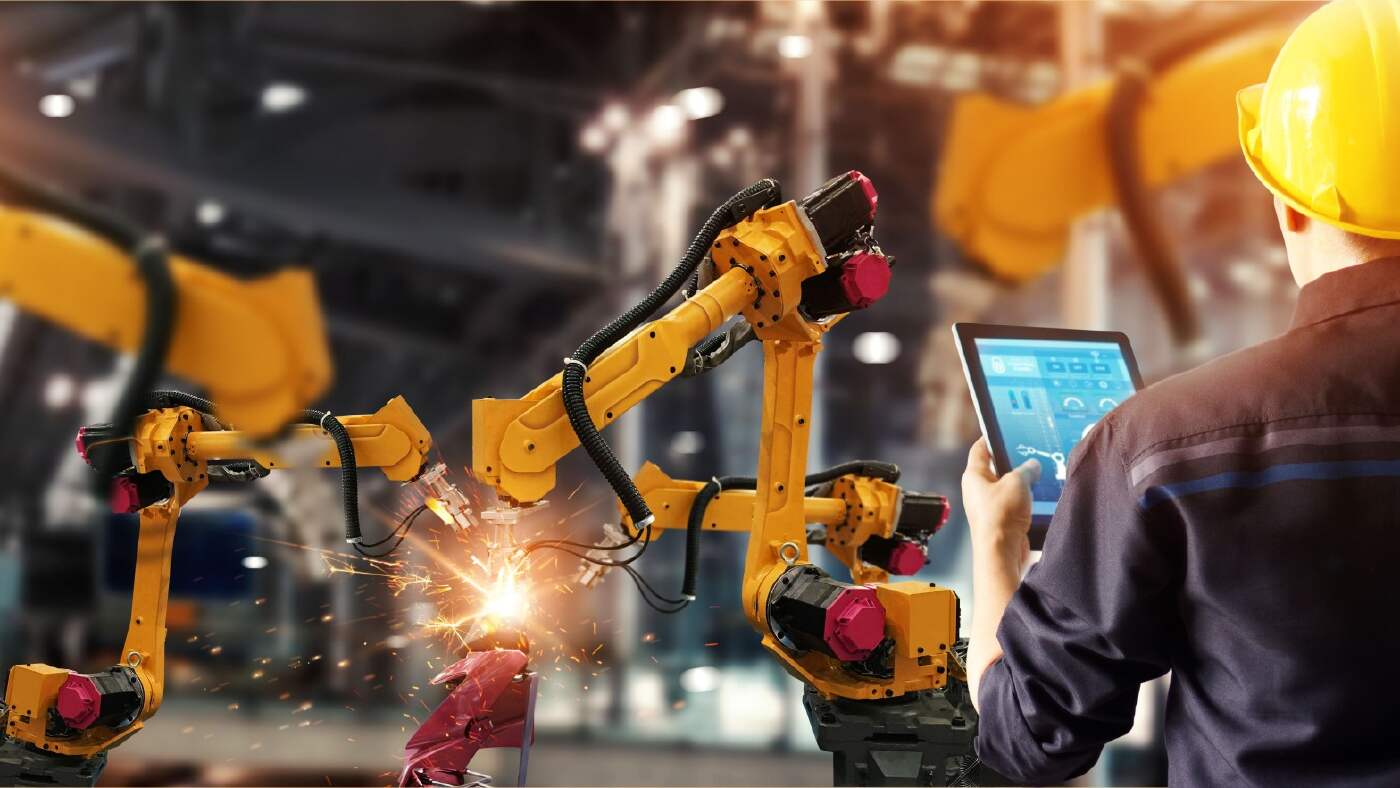
Aerospace robots are counted among the most advanced robotics systems in the world. Readily adopted by the aerospace industry for their accuracy, speed and precision, robotics aerospace systems can reduce waste and improve efficiency.
From drilling holes in fuselages to inspecting aircraft engines for faults, aerospace robots are involved at every stage of the design, manufacture and maintenance stage. Without them, the aerospace industry would struggle to build and fly airplanes and spacecraft.
In this article, we explore how robotics in aerospace engineering and robotics in aerospace manufacturing work.
What Is Engineering Aerospace Mechanical Robotics?
Engineering aerospace mechanical robotics refers to the robots and robotic systems employed by the aerospace industry. Automation and robotics aerospace systems are employed by aerospace engineers at almost all levels of the lifecycle of an aircraft.
Robots are needed to design the planes you take on holiday, while NASA uses robots to inspect their spacecraft and stations in orbit. Several key roles that aerospace robots undertake include the following tasks:
Manufacturing and Assembly
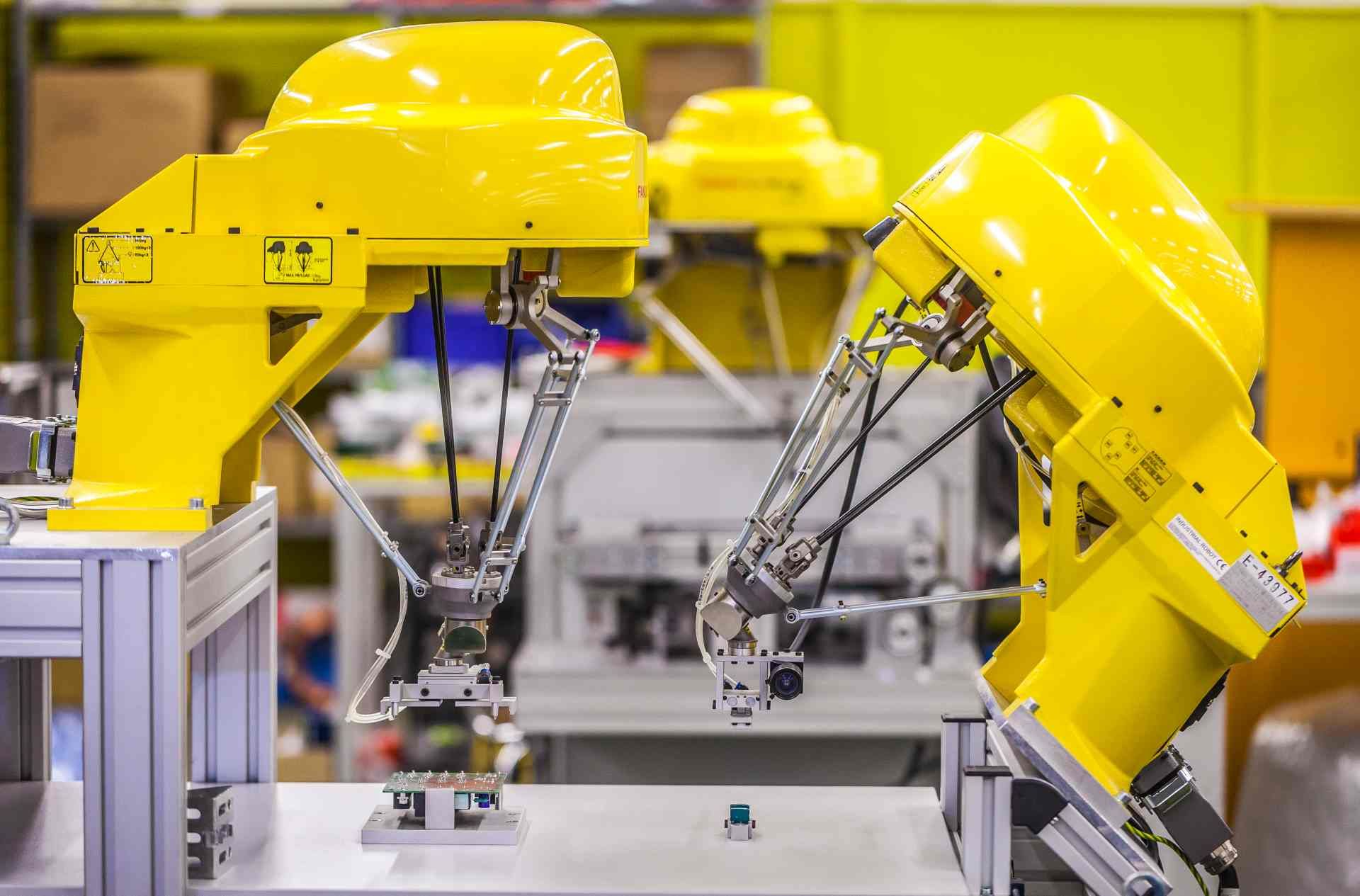
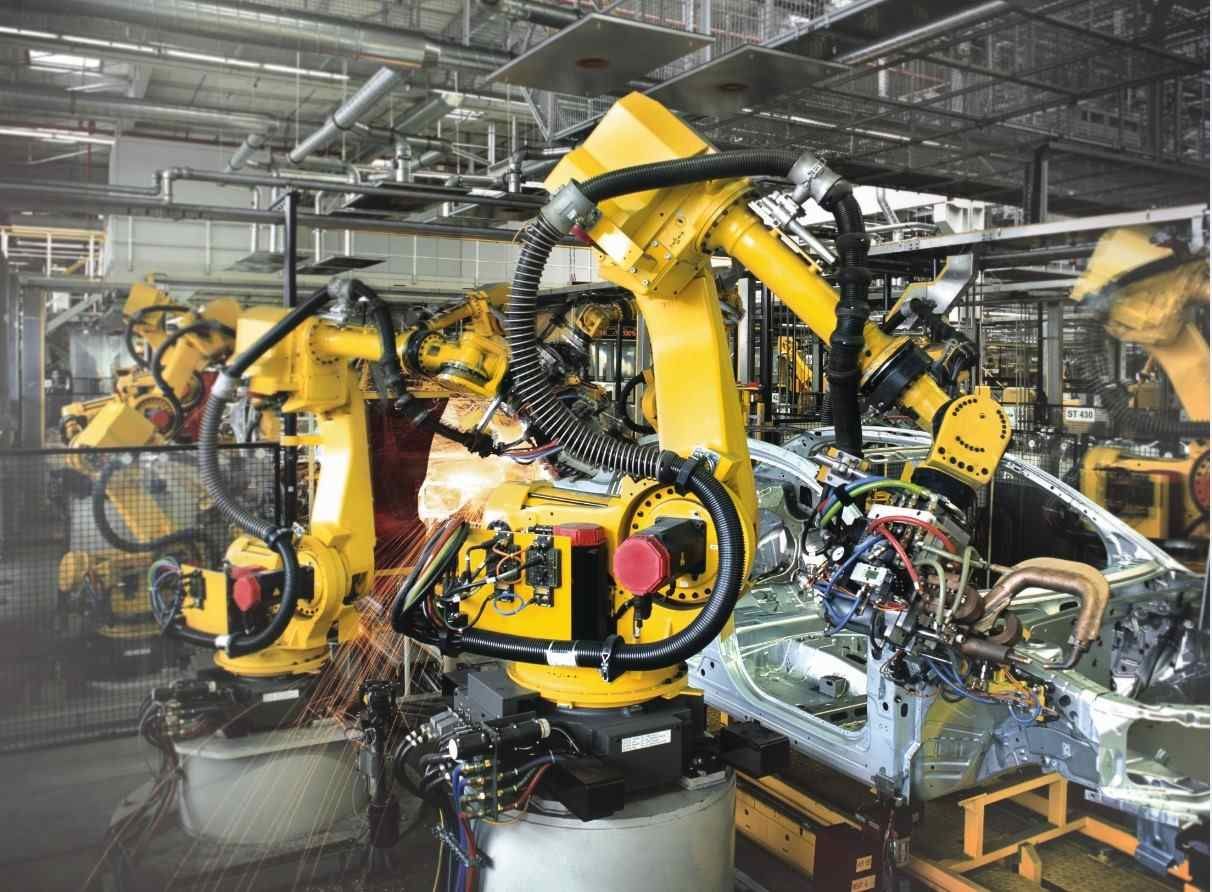
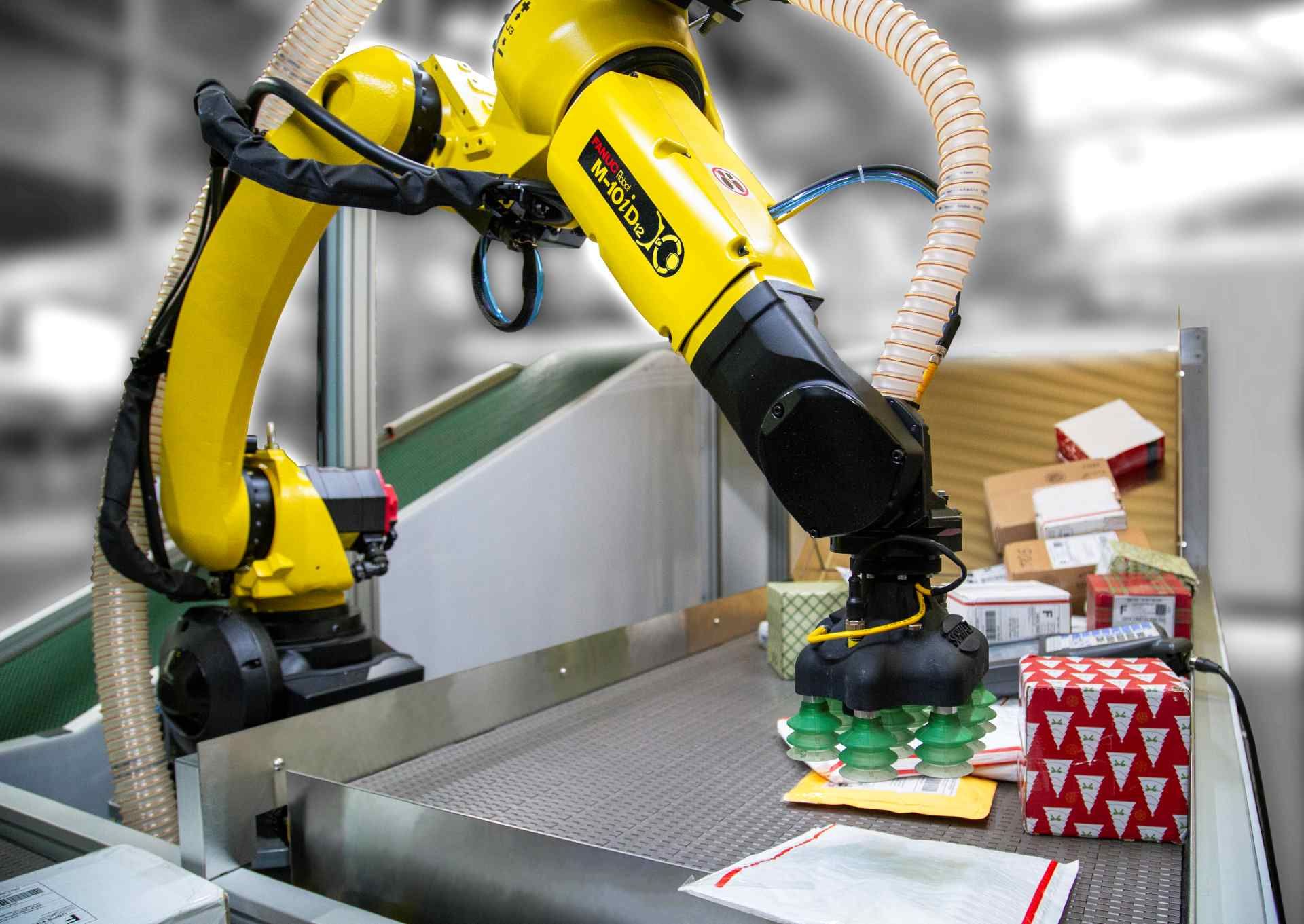
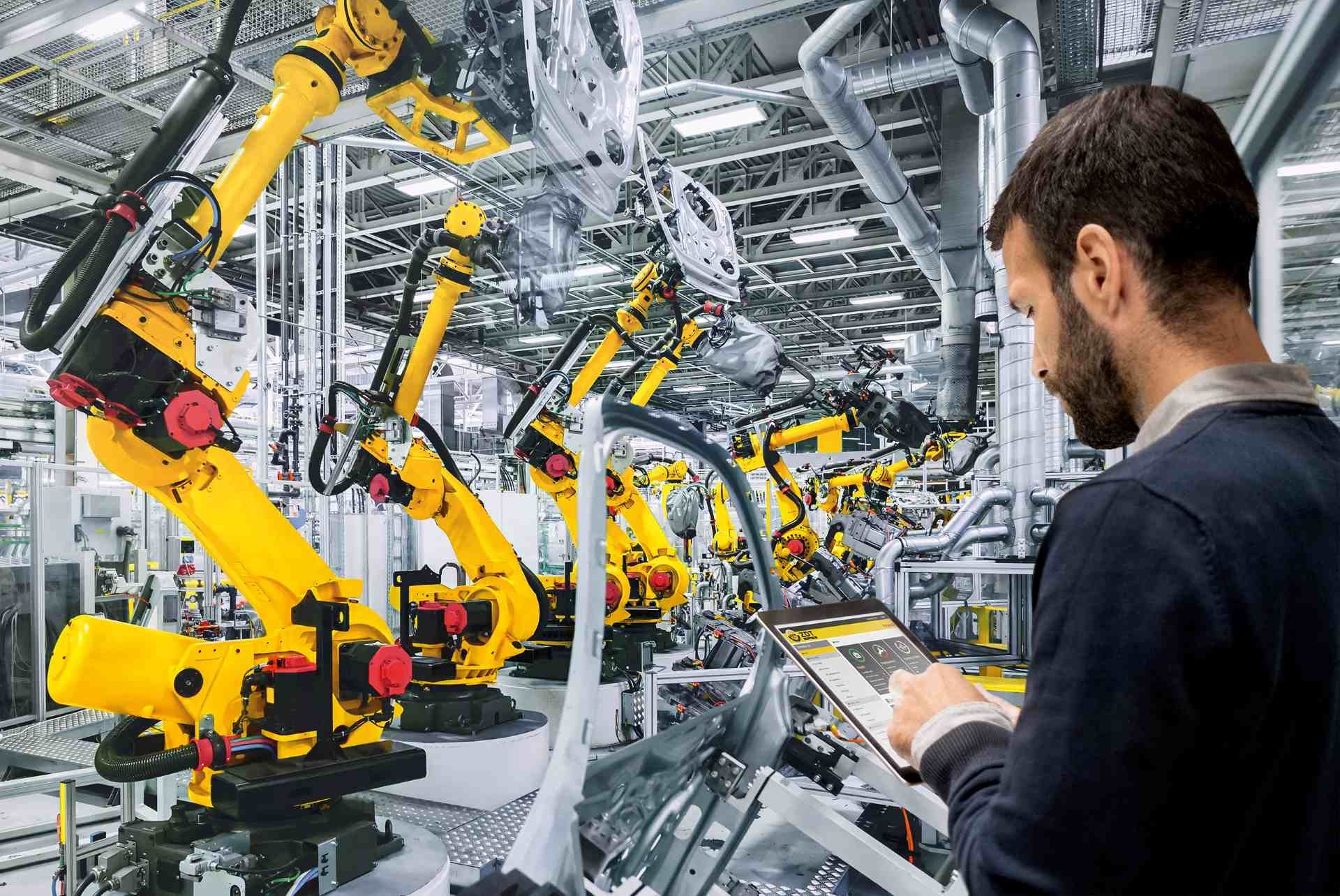
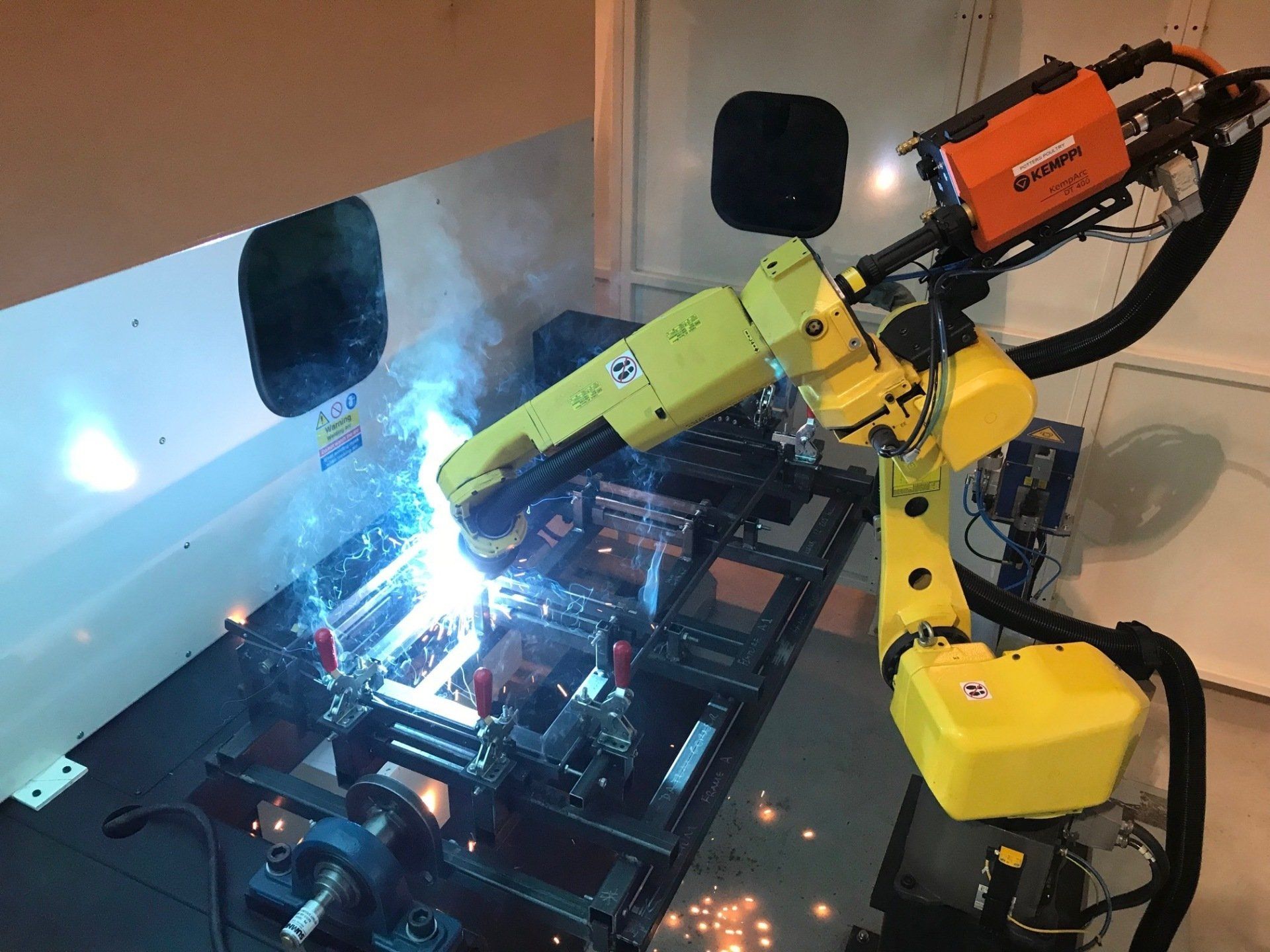
Manufacturing robots are one of the most common types of industrial robots, and they’re heavily utilised by the aerospace industry. Robotics in aerospace manufacturing often consists of versatile articulated robots, which are capable of mimicking human movements. These robots might be programmed to hold and operate welding equipment, and they’re commonly found on manufacturing and assembly lines.
Drilling
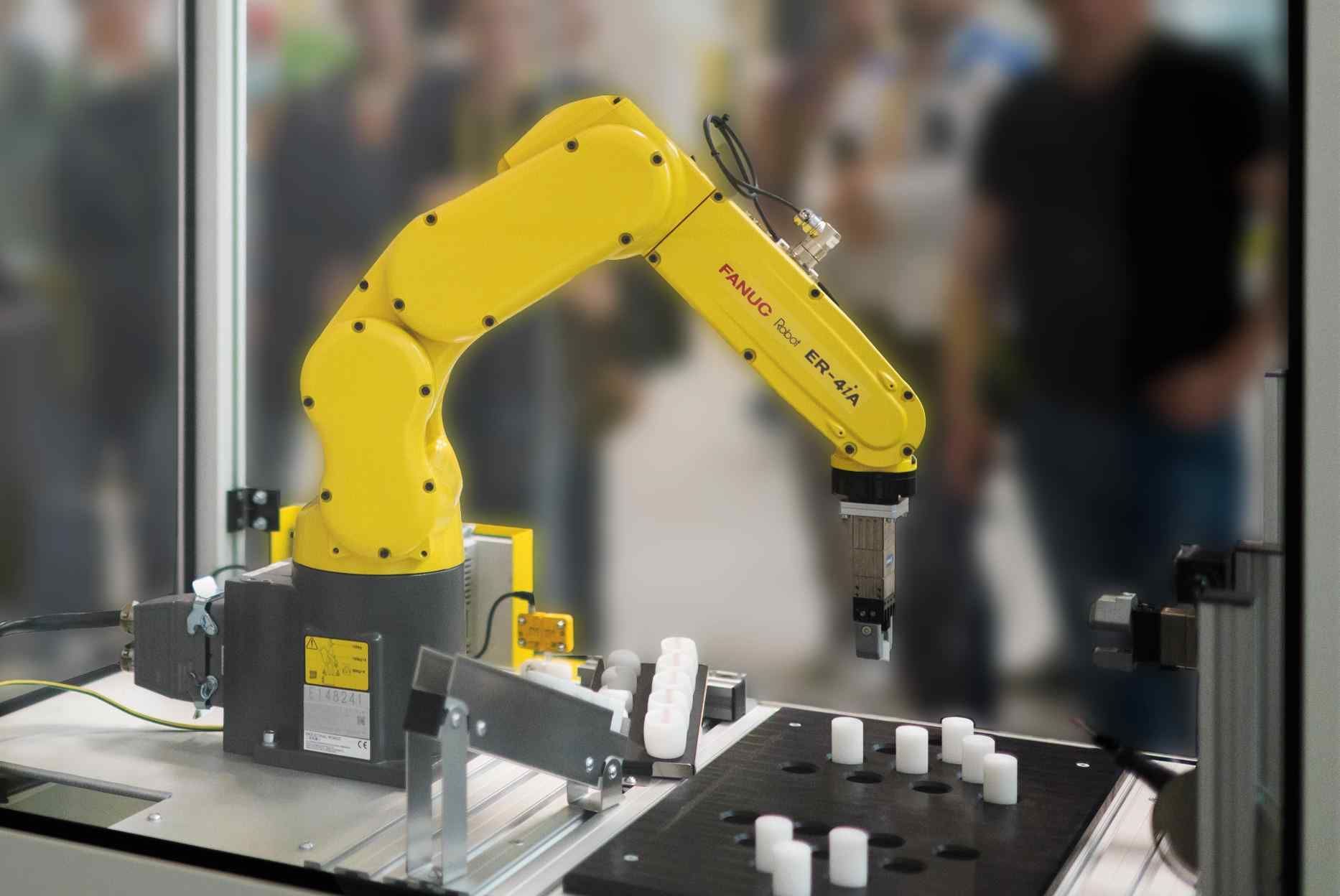
Aerospace robots are commonly used for drilling, a task which requires incredible levels of consistency when applied to aircraft manufacturing. Drilling robots are typically programmed to drill thousands of holes in the fuselage of aircraft, each one of which has to be precisely sized and located.
Painting
Aircraft are regularly painted as part of their upkeep, or when an aircraft company decides to change their branding or design. Aircraft have a huge surface area to paint, and this largely monotonous task is typically performed by robots instead of humans.
Inspection
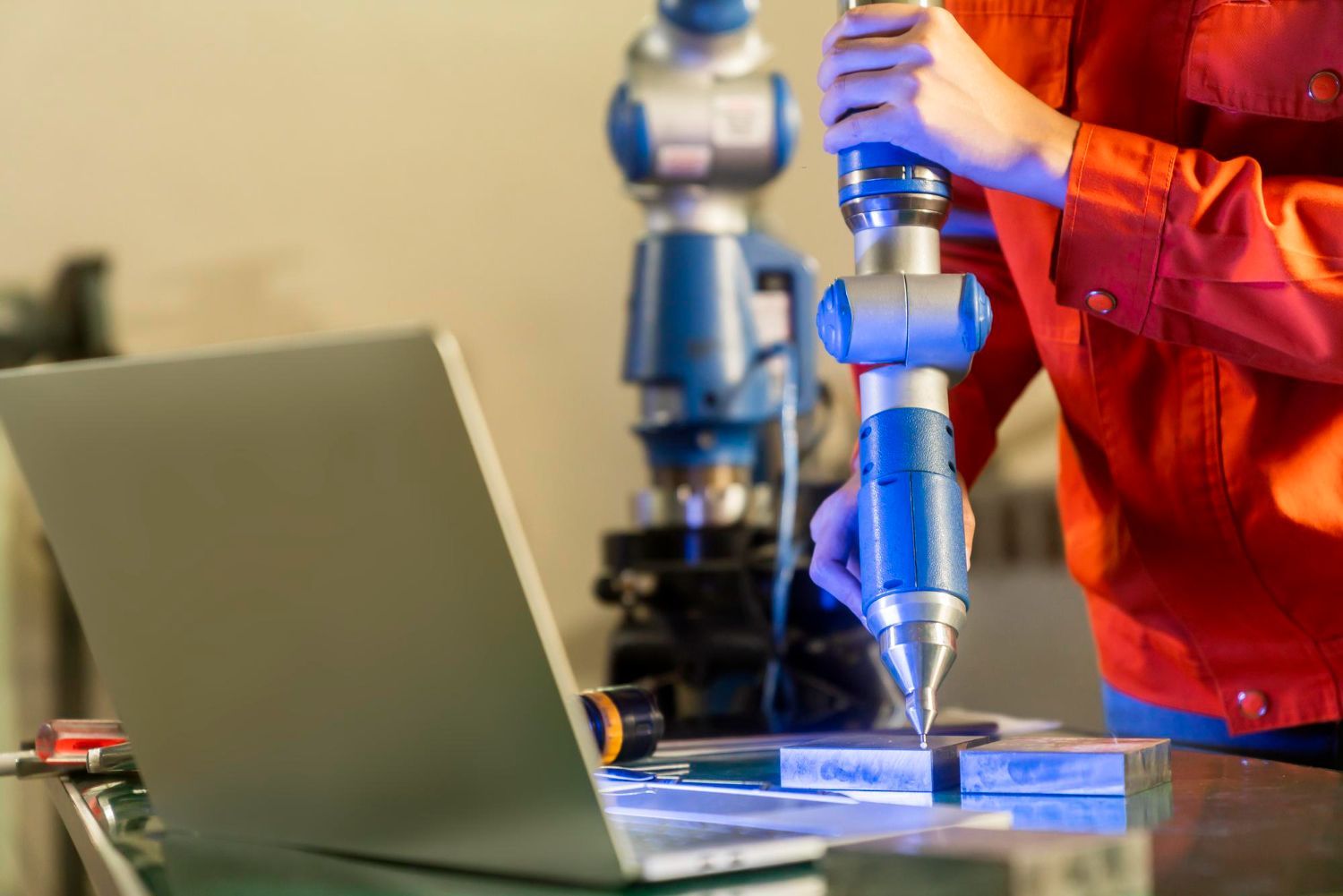
Aerospace robots can be programmed to undertake vital inspection tasks. NASA will use robots to inspect the exterior of spacecraft or space stations when they are in orbit, saving humans from making risky ventures outside. Aircraft manufacturers commonly use robots to inspect hard-to-reach areas
of an aircraft or to carry out hazardous tests on engines.
Who Created Aerospace Robots?
Aerospace robots are a relatively new addition to the robotics field, but they’re descended from a long line of manufacturing robots dating back to the 1950s.
The first manufacturing robot to see the workshop floor was named Unimate, and it was first patented in 1954. Unimate was a simple but effective robot that was readily adopted by General Motors on their assembly lines, where they helped weld die castings to car bodies.
Since then, robotics technology has only improved, and the aerospace industry has become one of the biggest users in the world. Industry leaders like FANUC Robotics have developed effective automation systems that have allowed robotics in aerospace manufacturing and robotics in aerospace engineering to become widespread.
Why You Should Use Robots in the Aerospace Industry
Aerospace robots have brought huge benefits to the design, manufacture and maintenance of aircraft and spacecraft. There are many reasons why robotics aerospace systems should be adopted, including:
- They improve accuracy during the production process
- Cut down on design, manufacturing and maintenance times
- Undertake tasks 24/7 with no need for breaks
- Produce consistent, high-quality results
- Reduce wasted materials and improve efficiency
- Perform repetitive and dangerous roles in place of humans
- Increase the need for higher-skilled supervisory and design roles for humans
How Do Aerospace Robots Work?
Any aerospace robotics engineer will tell you that the best robotics systems are bespoke. This means different robotics aerospace systems work in different ways, but they are typically designed using several key types of robots.
Aerospace robots might include the following:
- Articulated robots: Better known as robot arms. These mimic human movements.
- Cartesian robots: Operate up, down and horizontally across three axes.
- SCARA robots: Selective compliance assembly robot arms.
- Delta robots: Three robotic arms working in tandem.
These robots may operate individually or be programmed to work in tandem as part of a wider system, such as on a manufacturing line. The type of robot required depends on the task. For example, articulated robots are commonly used to hold welding machines.
Contact Cyber-Weld Today for More Information on Robotics In Aerospace Engineering
If you’d like to know more about robotics in aerospace engineering or robotics in aerospace manufacturing, our expert team is ready to help.
Cyber-Weld provides a comprehensive range of robotic services, including an extensive array of bespoke aerospace robots designed for industrial use.
Contact Cyber-Weld today to find out how we can help you.